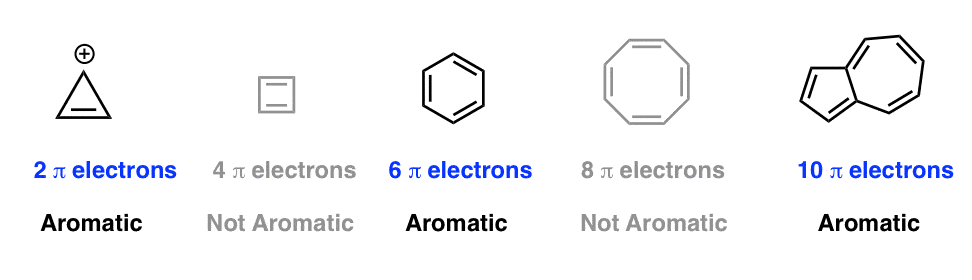
Huckel's 4n2 rule is used to determine if a planar, cyclic, conjugated system has aromatic character or stabilization A molecule is typically considered aromatic if it planar, cyclic, conjugated and has 4n2 π electrons where n=0, 1, 2, 3 etcThis rule is the work of the German theoretician, E Huckel, who devised the simple form of molecular orbital theory we have described in this chapter The theory is appropriately called Huckel MO theory, and the rule is Huckel's 4n 2 rule As Huckel formulated, the 4n 2 rule applies only to monocyclic systemsIt must be flat And, it must have a certain number of πelectrons (4n2 is Huckels rule);
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
Huckel 4n 2 rule
Huckel 4n 2 rule-In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry NCERT P Bahadur IITJEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan BiologyA cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its π electrons equals 4n 2 where n is zero or any positive integer (although clearcut examples are really only established for



Aromaticity The Huckel 4n 2 P Rule Youtube
Hückel's rule Planar monocyclic completely conjugated hydrocarbons will be aromatic when the ring contains 4n 2π electrons, where n ⇒ zero or any integer Thus, rings with 2,6,10,14 etc electrons are aromatic Benzene has 6 π electrons and is thus aromaticThe "4n 2 rule" is derived analytically at the level of the simple Hückel theory for neutral evenmembered chains, their double ions, as well as cations and anions of the oddmemberedThe lone pair of electrons assumes a sp2 hybridized orbital, making the molecule planar, adding 2 more electrons to the ring to give 4n2 pielectrons and creating the 5th pi orbital necessary to complete Huckel's Rule and results in an aromatic ion
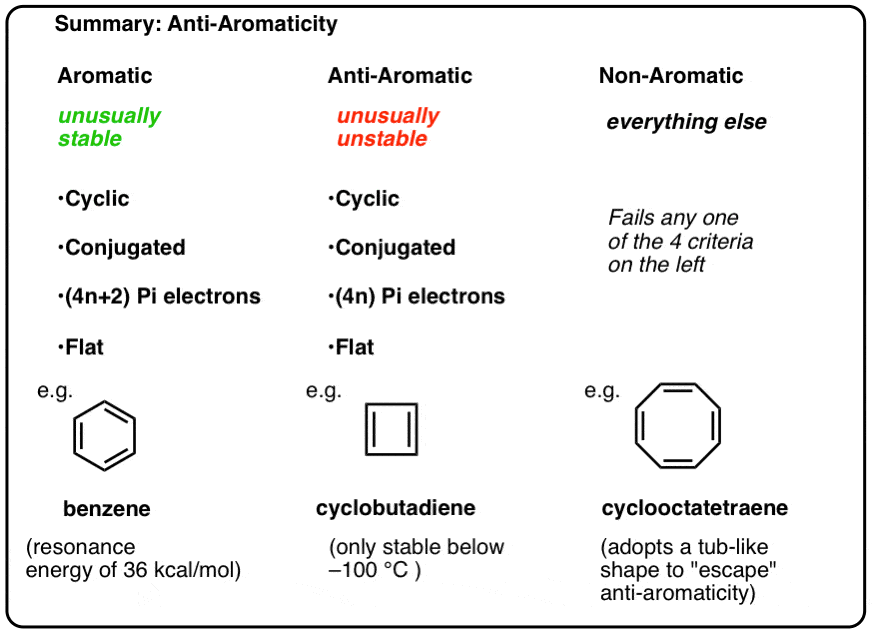
Cyclic, planar compounds with a fully conjugated 4n π electrons are called antiaromatic compounds So, both aromatic and antiaromatic compounds are cyclic, planar and fully conjugated and the only difference is the number of π electrons Huckel (4n2) – aromatic, Mobius (4n) – antiaromatic Charged Aromatic and Antiaromatic CompoundsHuckel's 4n2 rule is used to determine if a planar, cyclic, conjugated system has aromatic character or stabilization A molecule is typically considered aromatic if it planar, cyclic, conjugated and has 4n2 π electrons where n=0, 1, 2, 3 etcThe Huckel 4n 2 Pi Electron Rule A ringshaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula '4n 2' where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero)
A cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its π electrons equals 4n 2 where n is zero or any positive integer (although clearcut examples are really only established for,21 For triplet states, it is known that Huckel's 4n 2 rule is no longer valid in governing the propensity of aromaticity It is instead replaced by Baird's rule, 21, 22 which dictates thatDefine aromaticity in terms of the Hückel 4n 2 rule use the Hückel 4 n 2 rule to determine whether or not a given polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon should exhibit aromatic properties describe the difference in properties between an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as benzene, and a nonaromatic polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon, such as cyclobutadiene or cyclooctatetraene



Basic Organic Chemistry L7 Aromaticity Aromatic Anti Aromatic Non Aromatic Huckel 4n 2 Rule Youtube


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
Objectives After completing this section, you should be able to define aromaticity in terms of the Hückel 4n 2 rule;Benzene is stable and the electrons are delocalized 16In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931 The succinct expression as the 4n 2 rule has been attributed to W v E Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time


Solved Using The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Determine Which Of Th Chegg Com


Aromaticity Tutorial For Cyclic Charged And Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds
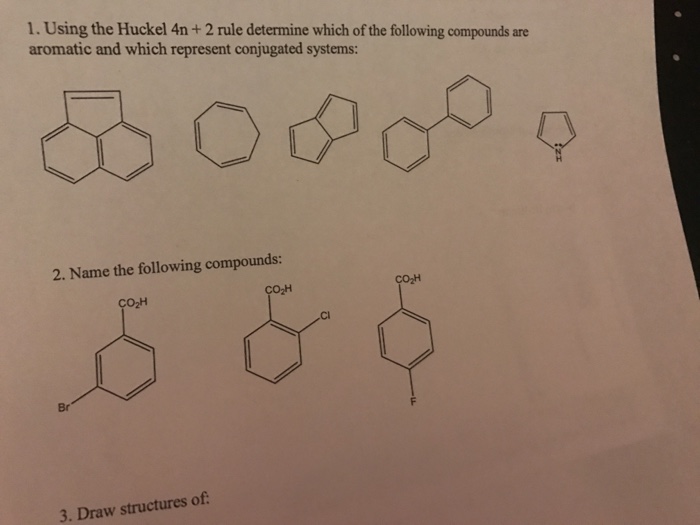
As Huckel formulated, the \(4n 2\) rule applies only to monocyclic systems However, as a practical matter it can be used to predict the properties of polycyclic conjugated polyenes, provided the important VB structures involve only the perimeter double bonds, as in the following examplesHuckel rule and its applications definition Huckel's Rule (4n2 rule) In order to be aromatic,a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals The pi electron count is defined by the series 4n2 where n = zero or a positive integer (0, 1, 2, etc)Use the Hückel 4 n 2 rule to determine whether or not a given polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon should exhibit aromatic properties describe the difference in properties between an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as benzene, and a nonaromatic polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon, such as cyclobutadiene or cyclooctatetraene



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps


A Disrotatory 4n 2 Electron Anti Aromatic Mobius Transition State For A Thermal Electrocyclic Reaction Henry Rzepa S Blog
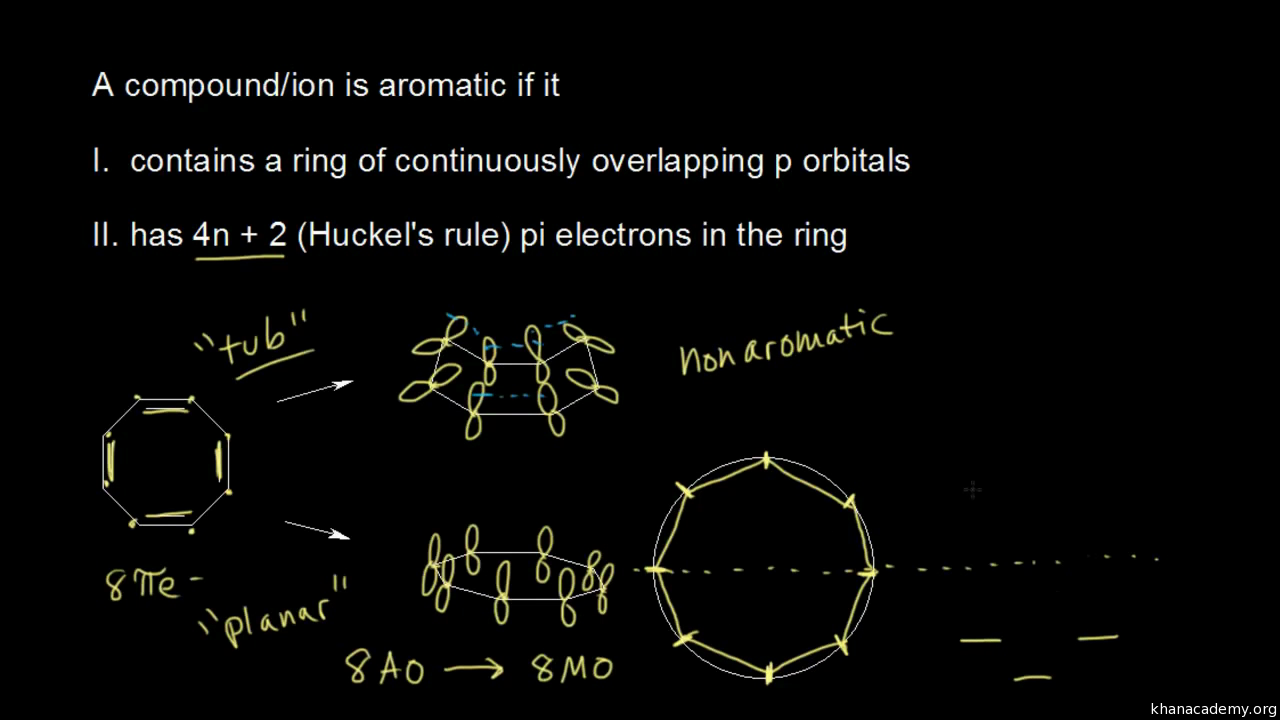
Furthermore, the 4n2 rule as indicator of aromatic stabilization should only be used in conjunction with the ring size;And this n is just algebra and not a characteristic of the molecule The number of pi electrons to be a multiple of 4n2 is one of the factors for aromaticity and not the only factor(4 n 2) rule is for checking weather compound is aromatic or not n = 1, 2, 3 where n represent α non fractionable number


Aromatic Stability Ii Video Khan Academy



In Huckel S 4n 2 Pi Rule For Aromaticity N Represents
Hückel's Rule In 1931, Erich Hückel postulated that monocyclic (single ring) planar compounds that contained carbon atoms with unhybridized atomic p orbitals would possess a closed bond shell of delocalized π electrons if the number of π electrons in the molecule fit a value of 4 n 2 where n equaled any whole numberIn keeping with the MöbiusHückel concept, a cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its πelectrons equals 4n 2 where n is a nonnegative integer, although clearcut examples are really only established for values of n = 0 up to about n = 6Huckel's Rule (4n2 rule) In order to be aromatic, a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons (electrons with pi bonds, or lone pairs within p orbitals) within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals



An Extension Of The Huckel 4n 2 Rule To Polycyclic Non Alternant Conjugated Hydrocarbons Pdf Document



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Huckels Rule 4n 2 Heterocycles Aromaticity Cute766
Use the Hückel 4 n 2 rule to determine whether or not a given polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon should exhibit aromatic properties describe the difference in properties between an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as benzene, and a nonaromatic polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon, such as cyclobutadiene or cyclooctatetraeneIn 1931, German chemist and physicist Erich Hückel proposed a rule to determine if a planar ring molecule would have aromatic properties This rule states that if a cyclic, planar molecule has 4 n 2 π electrons, it is aromatic This rule would come to be known as Hückel's Rule Four Criteria for AromaticityThe nature of the occupied π orbitals must always be examined


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term


Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
A cyclic ring molecule follows Huckel's rule when the number of its pi electrons equals 4n2 where n is zero or any positive interger (although clearcut examples are really only established for(organic chemistry) Aromatic (ring) compounds must have 4 n 2 pibonding electrons, where n is a whole number and generally limited to n = 0 to 5 When n = 1, for example, there are six pielectrons, as for benzene Also known as Hückel's ruleHuckel's rule, 4n plus 2, I have 6 pi electrons So if n is equal to 1, Huckel's rule is satisfied Because I would do 4 times 1, plus 2 And so I would get a total of 6 pi electrons And so 6 pi electrons


Pericyclic Reaction Selection Rules


15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry NCERT P Bahadur IITJEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan BiologyDescribe the difference in properties between an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as benzene, and a nonaromatic polyunsaturated cyclicIn an attempt to describe and rationalize the elusive aromatic properties of graphene by firstprinciples calculations in a simple and transparent way, we have constructed numerous judicially chosen realspace models of various sizes and symmetries, which lead to the aromaticity pattern of infinite graphene by a process of "spatial" evolution through successive peripheral additions, characterized by fundamental periodicities related to the traditional Huckel (4 n 2)π electron rule



Aromaticity



Huckel S Molecular Orbital Theory Huckel S Rule Extended Huckel
Use the Hückel 4n 2 rule to determine whether or not a given polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon should exhibit aromatic properties;In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931 The succinct expression as the 4n 2 rule has been attributed to W v E Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same timeBenzene is stable and the electrons are delocalized 16
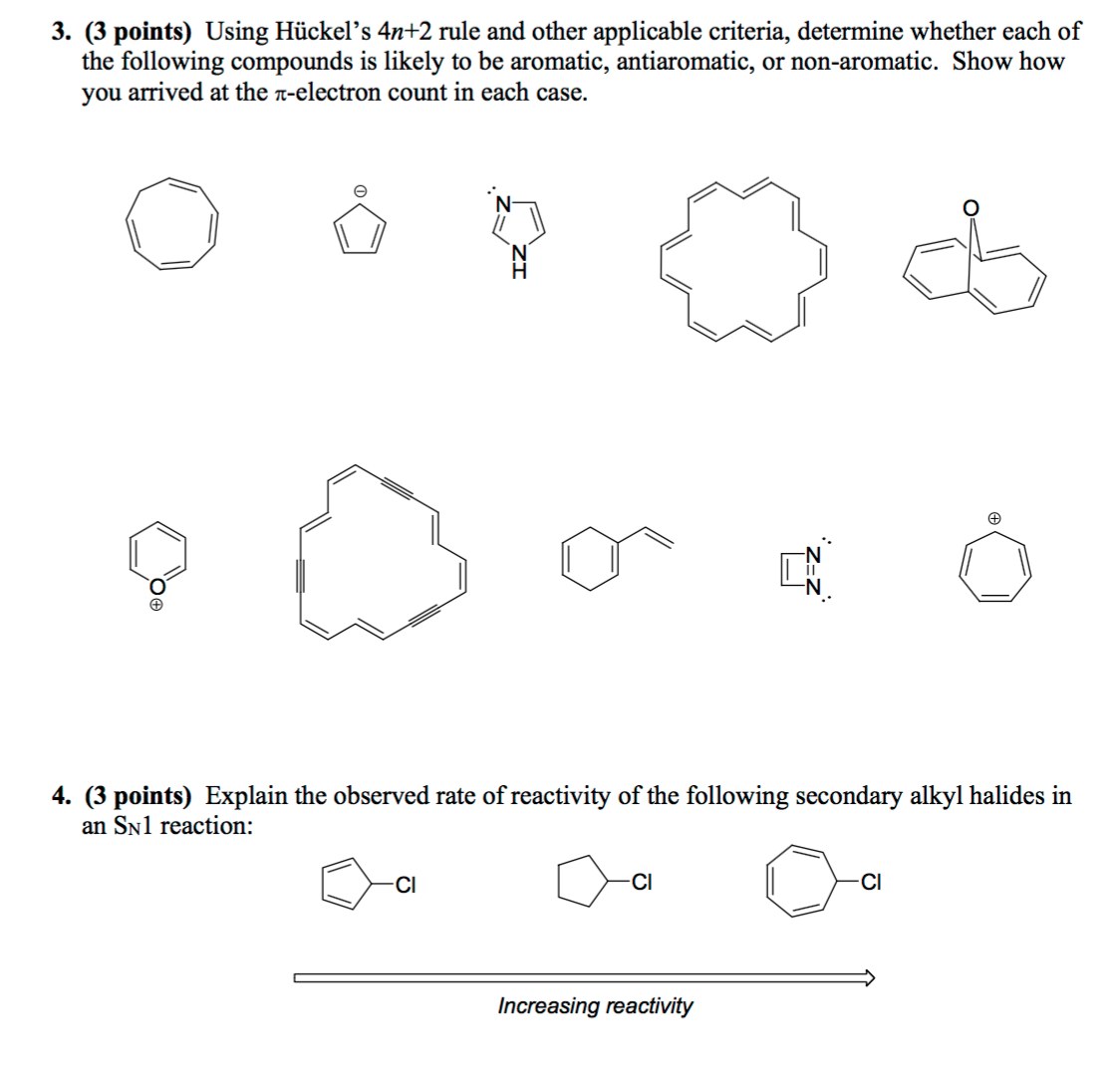


Solved Using Hu Ckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cri Chegg Com



Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples
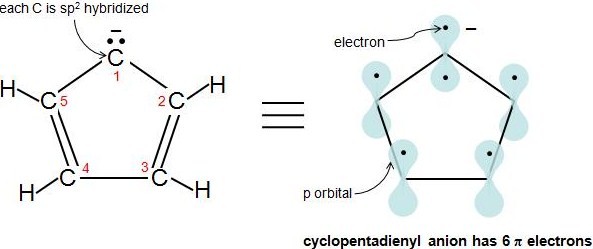
An sp 2 hybridized atom only has 1 p orbital, which can only hold 2 electrons, so we know that 1 electron pair is in the p orbital, while the other pair is in an sp 2 orbital So, only 1 of oxygen's 2 lone electron pairs are π electrons Furan has 6 π electrons and fulfills the 4n2 ruleHuckel's Rule (4n2 rule) In order to be aromatic,a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals The pi electron count is defined by the series 4n2 where n = zero or a positive integer (0, 1, 2, etc) The most common examples are Furan, Pyrolle, Naphthalene, Anthracene etc,21 For triplet states, it is known that Huckel's 4n 2 rule is no longer valid in governing the propensity of aromaticity It is instead replaced by Baird's rule, 21, 22 which dictates that


15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps
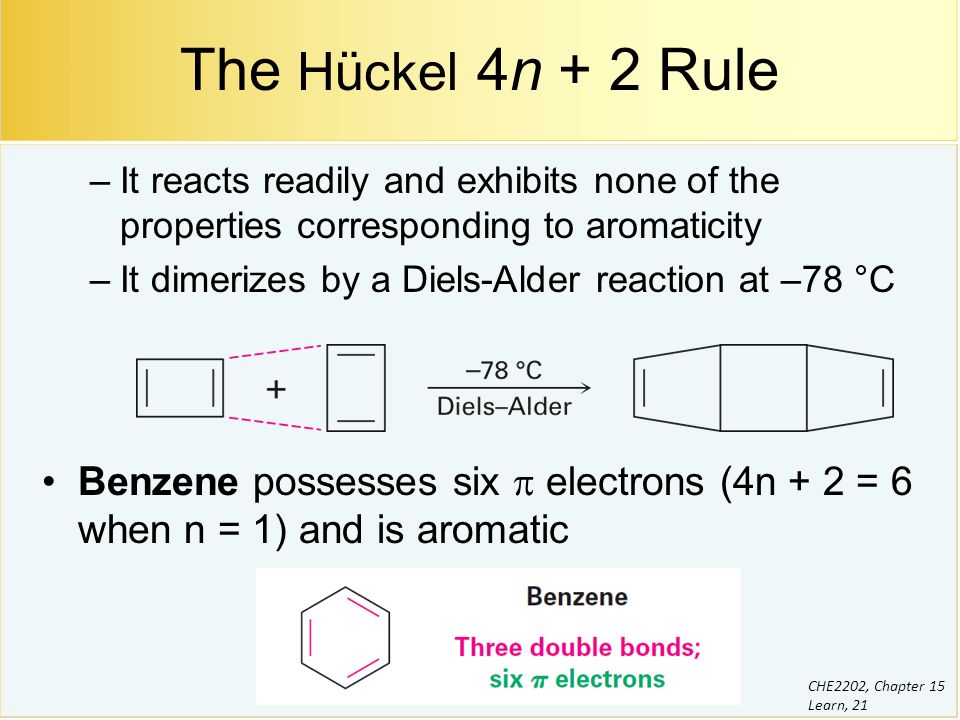
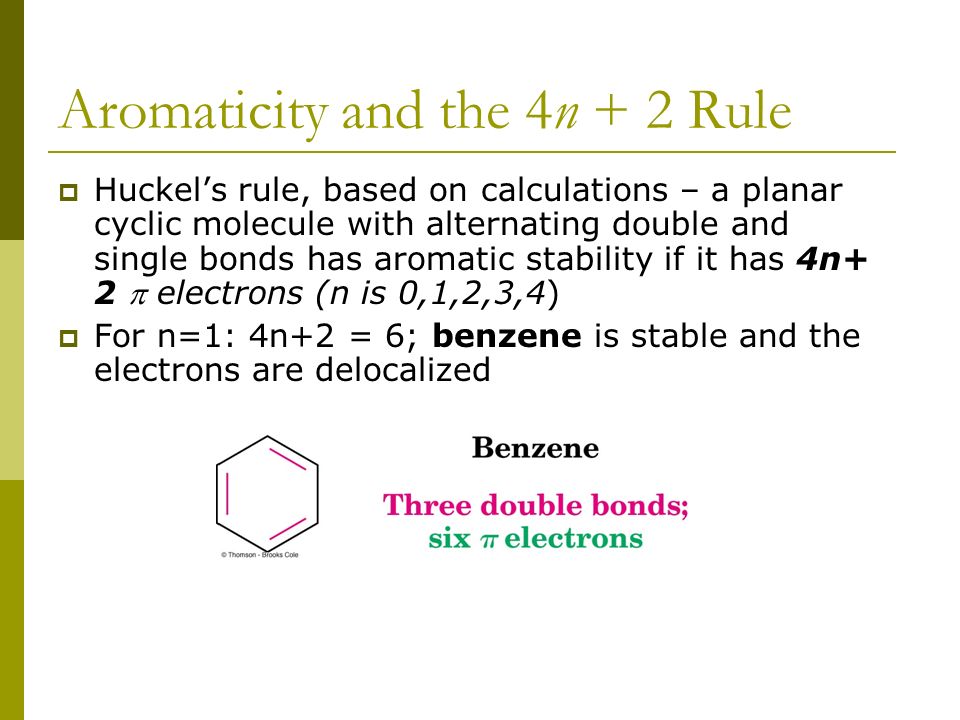
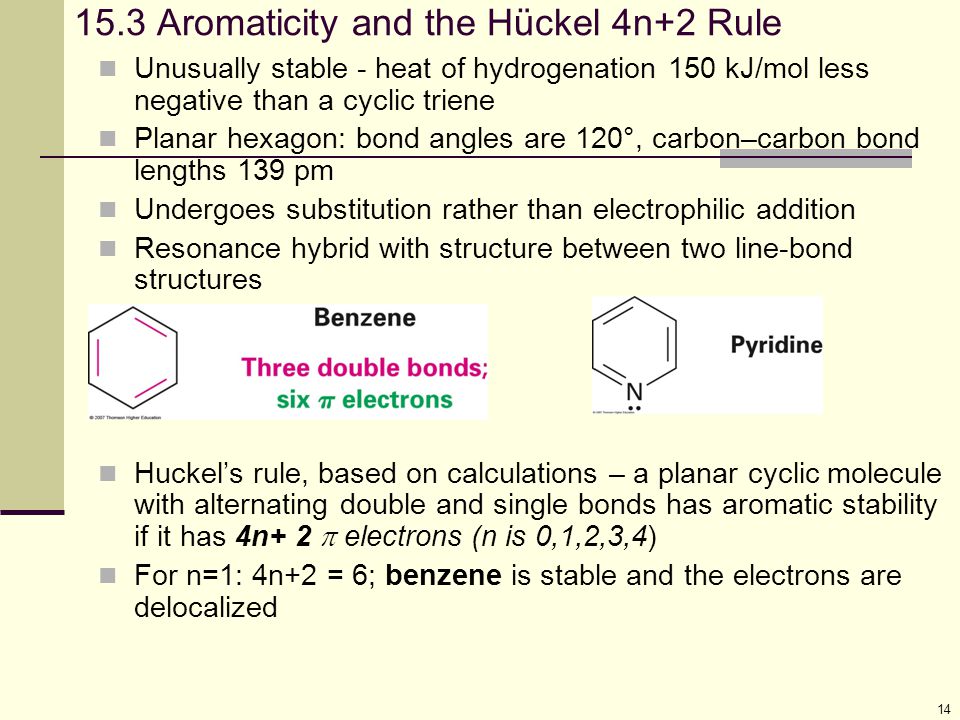
The Huckel 4n2 rule 32 Electrocyclic reactions, Cycloaddition reactions, Sigma tropic reactions 4 Macromolecules (6 hours) 41 Chainreaction polymerization mechanism free radical, ioniccationic and anionic, Coordination polymerization Condensation polymerization, Ring opening polymerization 42 Natural PolymersAromaticity and the 4 n 2 Rule • Huckel's rule, based on calculations – a planar cyclic molecule with alternating double and single bonds has aromatic stability if it has 4n 2 electrons (n is 0,1,2,3,4) • For n=1 4n2 = 6;If I think about Huckel's rule, 4n plus 2, I have 6 pi electrons So if n is equal to 1, Huckel's rule is satisfied Because I would do 4 times 1, plus 2 And so I would get a total of 6 pi electrons And so 6 pi electrons follows Huckel's rule If we look at the frost circle and we look at the molecular orbitals, we can understand Huckel's



Huckel S Rule For Aromaticity Time Saving Shortcut Youtube



Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples
An aromatic compound has a cyclic planar structure with (4n2)π electron clouds which give unusual stability to the compound due to the delocalization of π eAromaticity and the 4 n 2 Rule • Huckel's rule, based on calculations – a planar cyclic molecule with alternating double and single bonds has aromatic stability if it has 4n 2 electrons (n is 0,1,2,3,4) • For n=1 4n2 = 6;In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931 The succinct expression as the 4n 2 rule has been attributed to W v E Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time
.jpg?revision=1)


15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts


What Is 4n 2 P Rule Quora
Simply put, Huckel's rule for aromaticity states that a monocyclic system will be aromatic if there are 4n 2 delocalised electrons, (n an integer) contained within it eg 2, 6, 10, 14 etcIn this paper, esteemed Harvard chemist William Eggers von Doering succinctly summarized the Huckel rule as 4n 2 pi electrons (although writes it (2n4 here) in his synthesis of cycloheptatrienylium oxide ("tropone")So you take all the pi electrons and lone pairs (when applicable to be included) and set them equal to 4n2 electrons For example the number 10 is a huckel number because 4n2=10 n=2 and as long as n=0,1,2 (an integer) it passes the test



Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule 4n 2 Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule Aromaticity Youtube
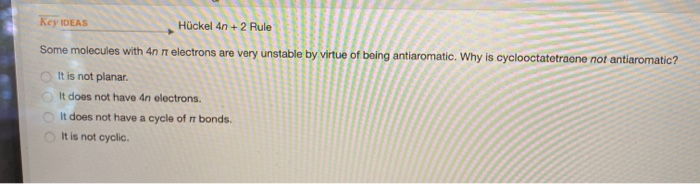


Solved Key Ideas Huckel 4n 2 Rule Some Molecules With 4 Chegg Com
The Huckel 4n2 rule 32 Electrocyclic reactions, Cycloaddition reactions, Sigma tropic reactions 4 Macromolecules (6 hours) 41 Chainreaction polymerization mechanism free radical, ioniccationic and anionic, Coordination polymerization Condensation polymerization, Ring opening polymerization 42 Natural PolymersHückel (4n 2) rule https//doiorg//goldbookH Monocyclic planar (or almost planar) systems of trigonally (or sometimes digonally) hybridized atoms that contain (4 n 2) πelectrons (where n is a nonnegative integer) will exhibit @A@ characterThe "4n 2 rule" is derived analytically at the level of the simple Hückel theory for neutral evenmembered chains, their double ions, as well as cations and anions of the oddmembered chains, by
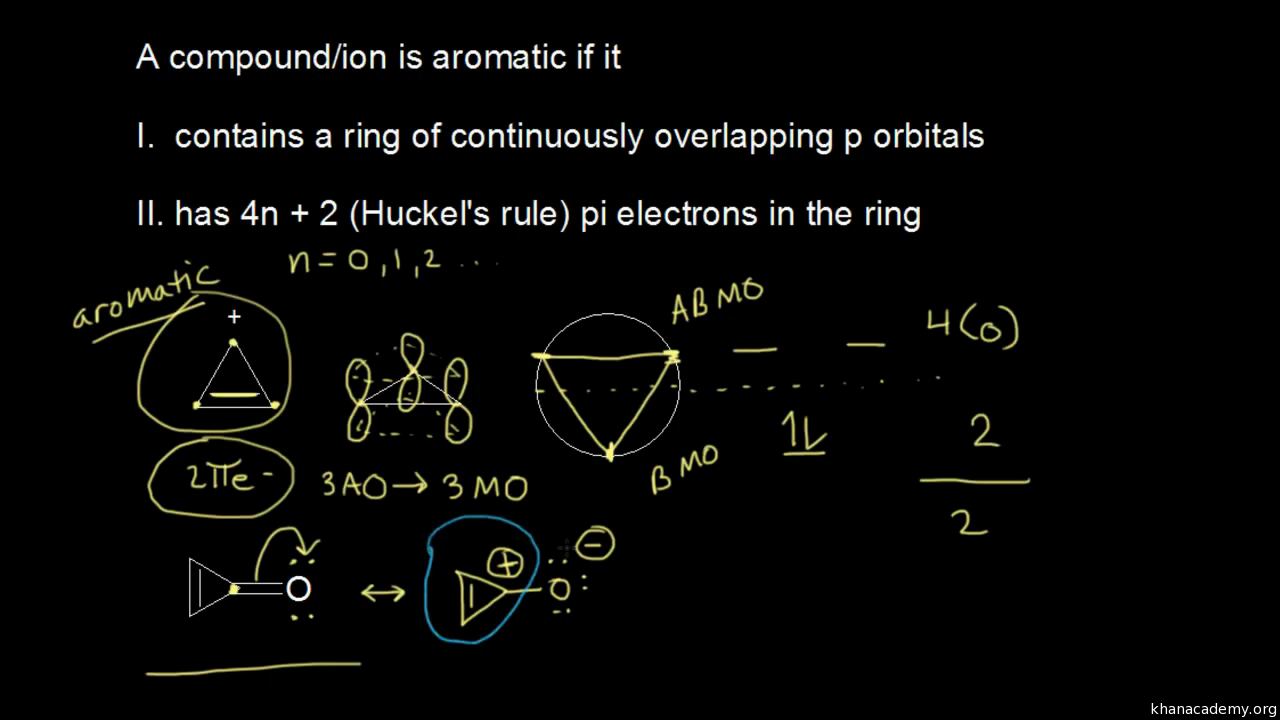


Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy



Pdf Analytical Derivation Of The Huckel 4 N 2 Rule
Huckel's rule was given by German physicist and physical chemistry Erich Huckel in 1931 Although its succinct formulation as 4n 2 was given by Professor William von Eggers Doering It is also known as Huckel's 4n 2 pi electrons rule Before understanding the Huckel's rule, you need to have a good understanding of aromaticity
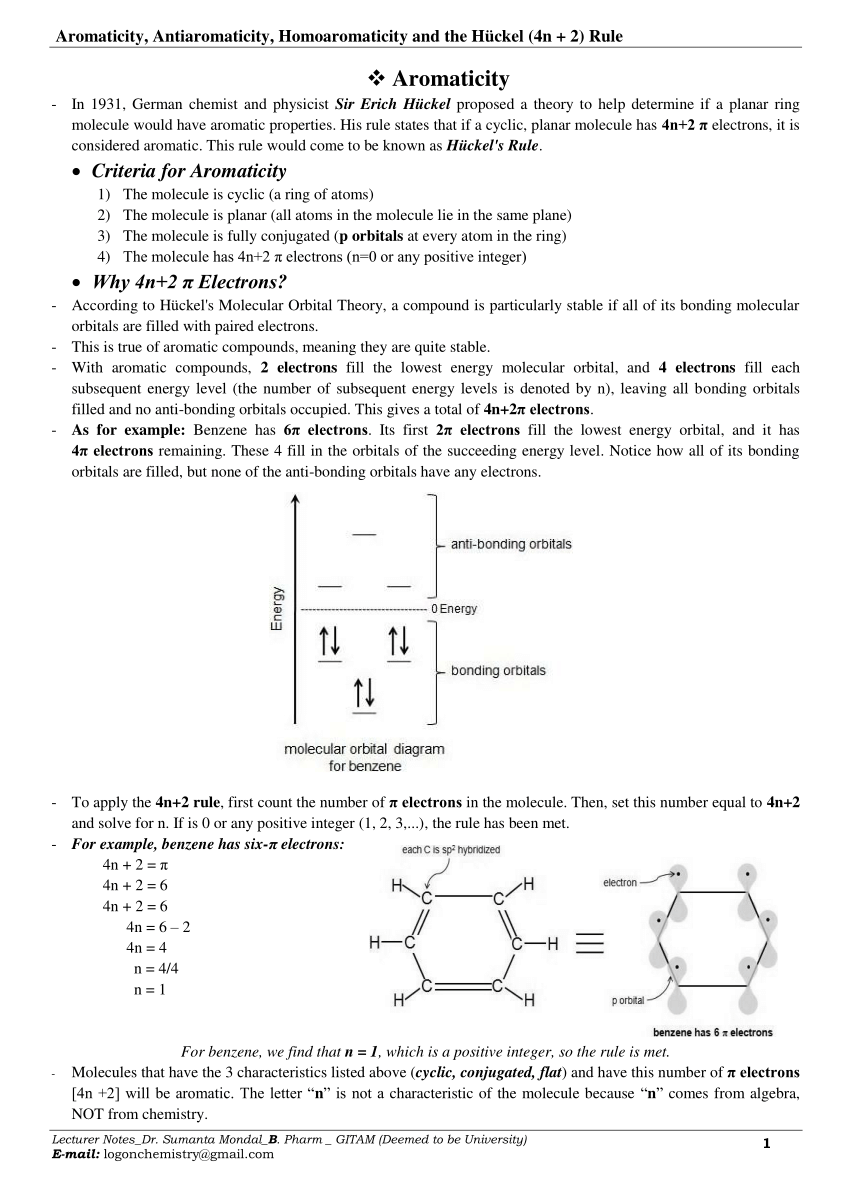


Pdf Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Homoaromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule



109 Aromaticity 2 Huckel S Rule Madoverchemistry Com



In Huckel S 4n 2 Pi Rule For Aromaticity N Represents
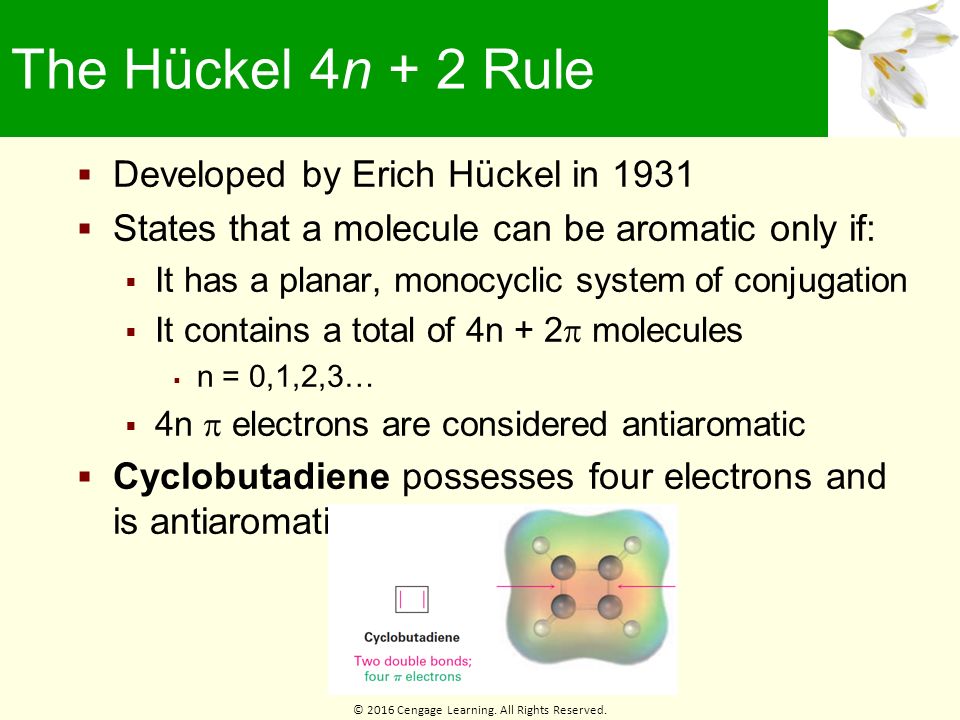


Chapter 15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Download
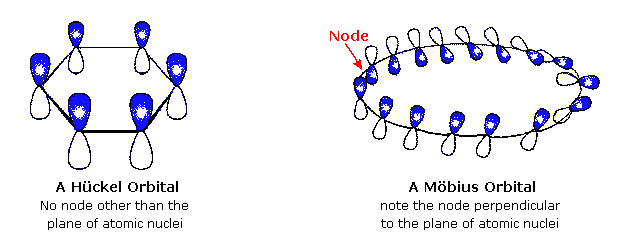


A Mobius 16 Pi Electron System
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=440&height=181)


15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts



Ch 15 Benzene Reactivity Huckel S Rule 4n 2 P Electrons Aromatic Ppt Video Online Download



Solved Using The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Determine Whether Each Chegg Com



Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep



Aromatic Substitution Reactions Reactions Nomenclature Ppt Download
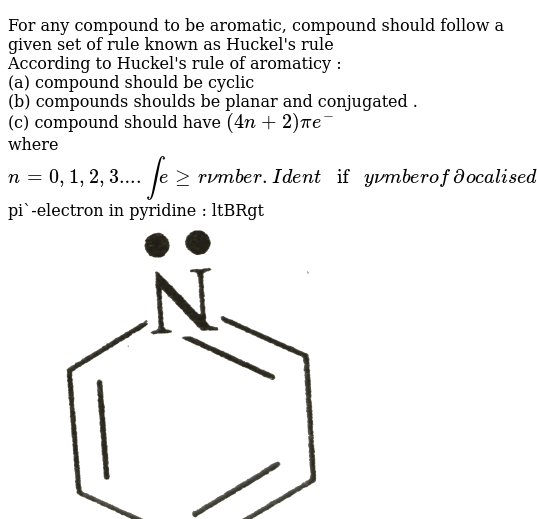


For Any Compound To Be Aromatic Compound Should Follow A Give
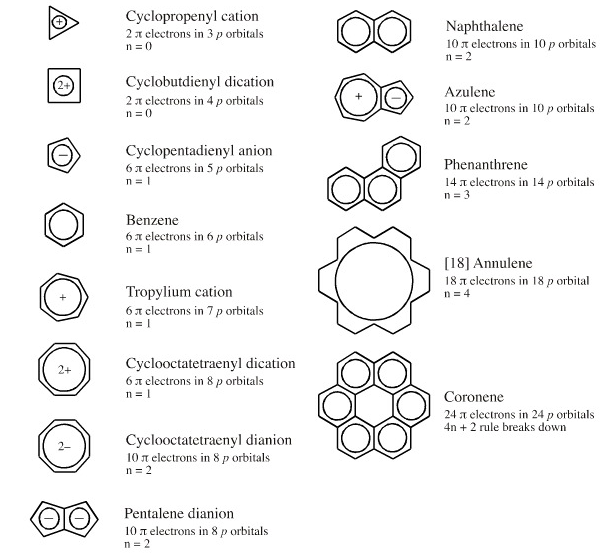


Lewis Theory Chemogenesis



Solved 1 According To Huckel S Rule How Many Pi A 4n 2 Chegg Com



Global Aromaticity In Macrocyclic Polyradicaloids Huckel S Rule Or Baird S Rule Accounts Of Chemical Research X Mol
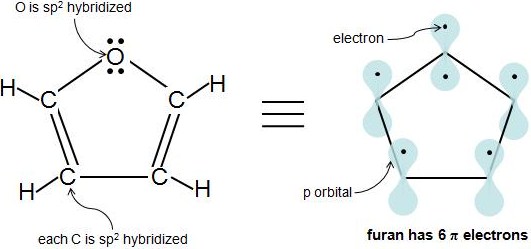.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=369&height=173)


15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts
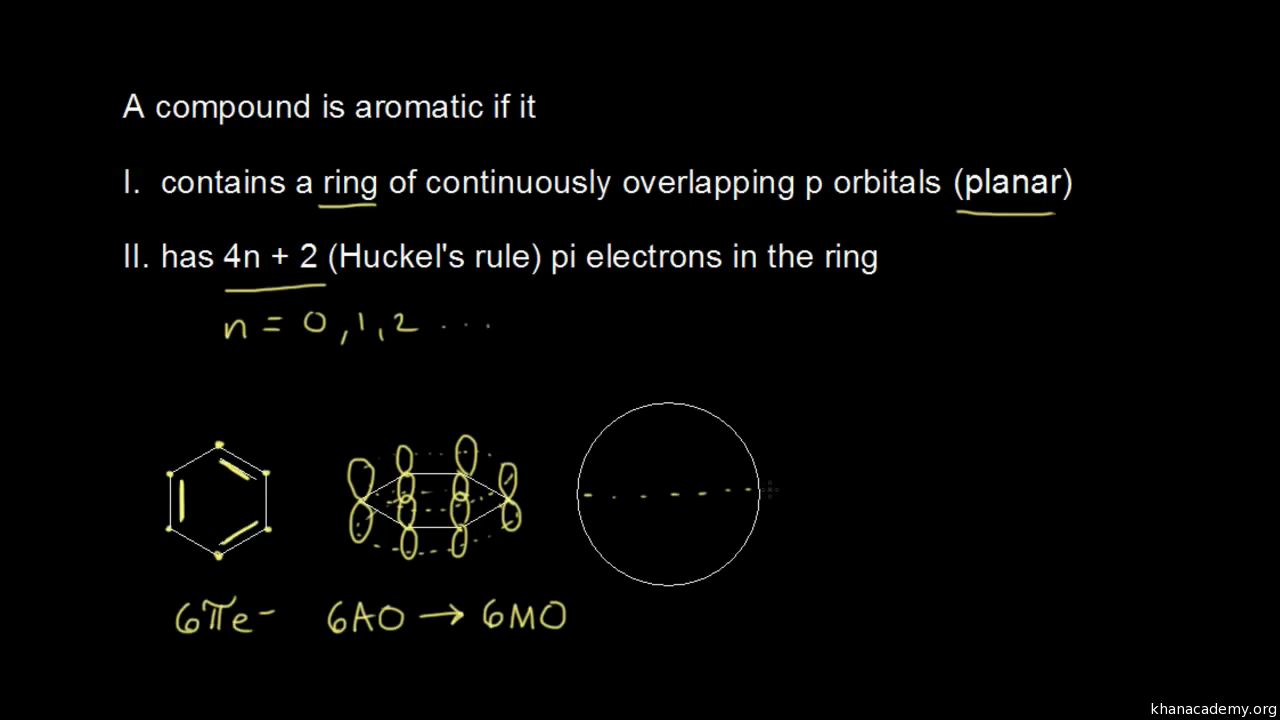


Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy


Solved Question 18 The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Describes The Num Chegg Com
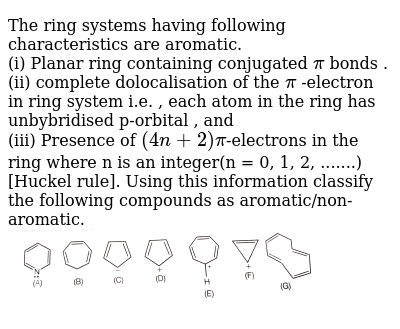


In Huckel S Rule 4n 2 P Electrons What Does N Signifies



Aromaticity The Huckel 4n 2 P Rule Youtube
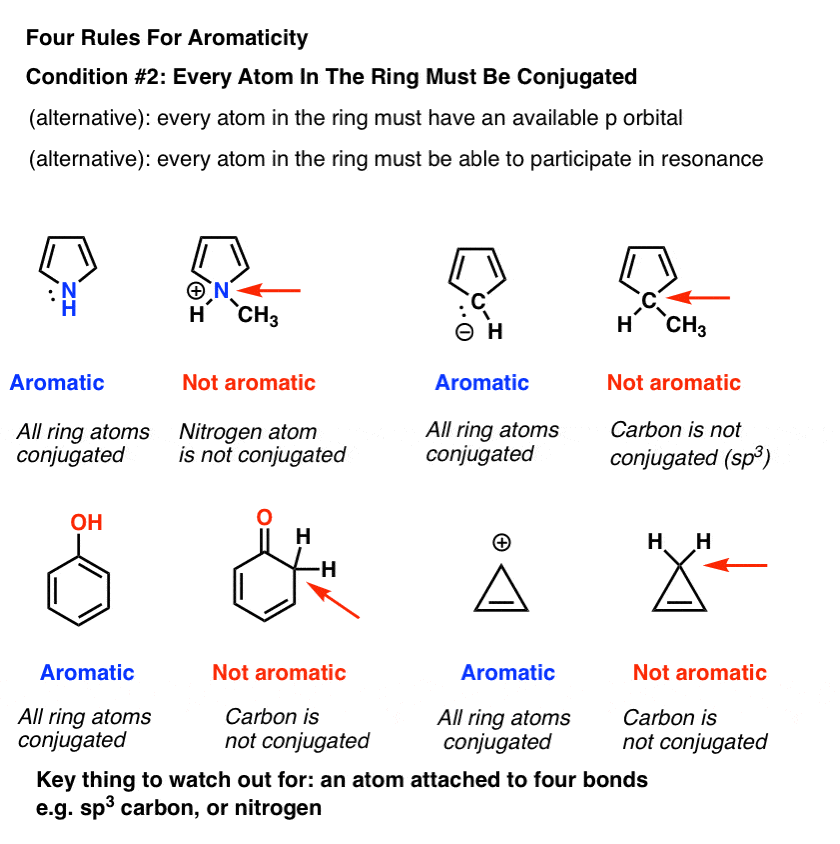


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry



Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry



What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
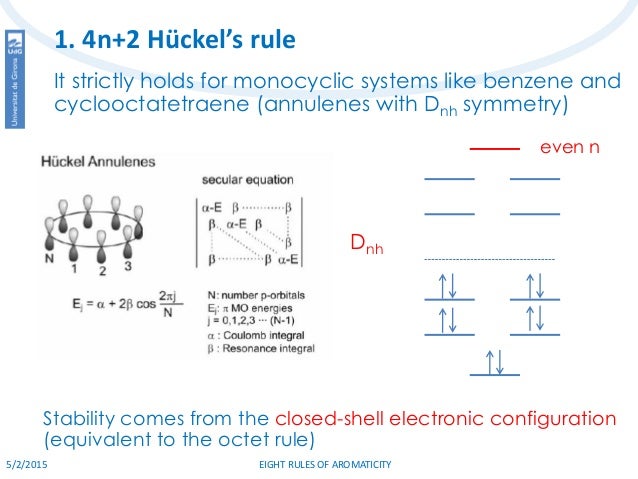


Eight Rules Of Aromaticity
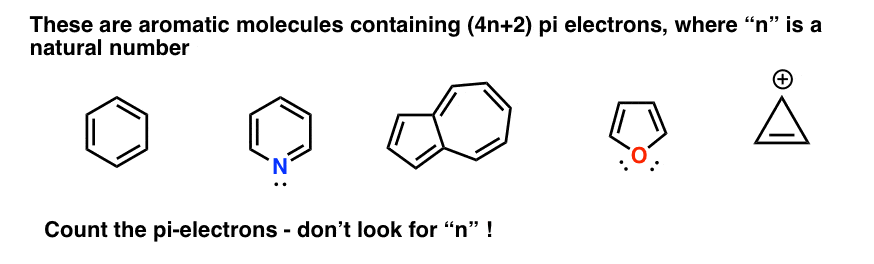


Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
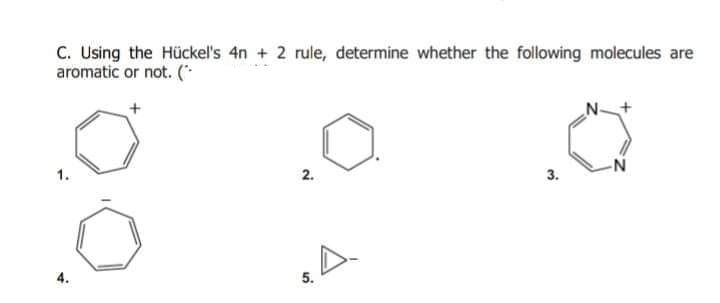


Answered C Using The Huckel S 4n 2 Rule Bartleby



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Non Aromatic 13 Worked Examples



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps
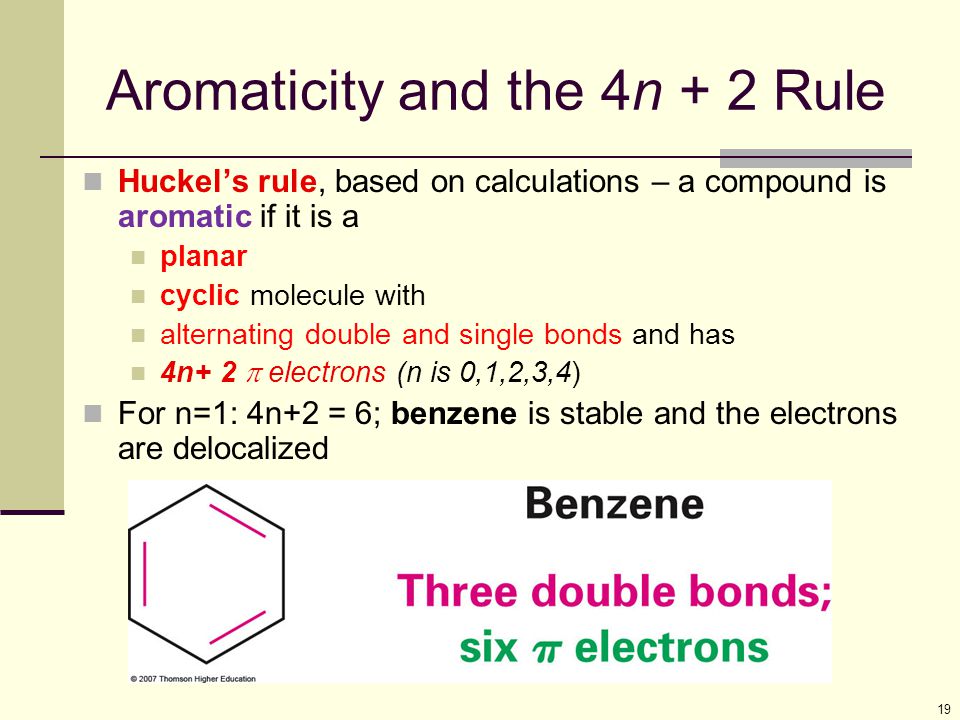


15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download


Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help
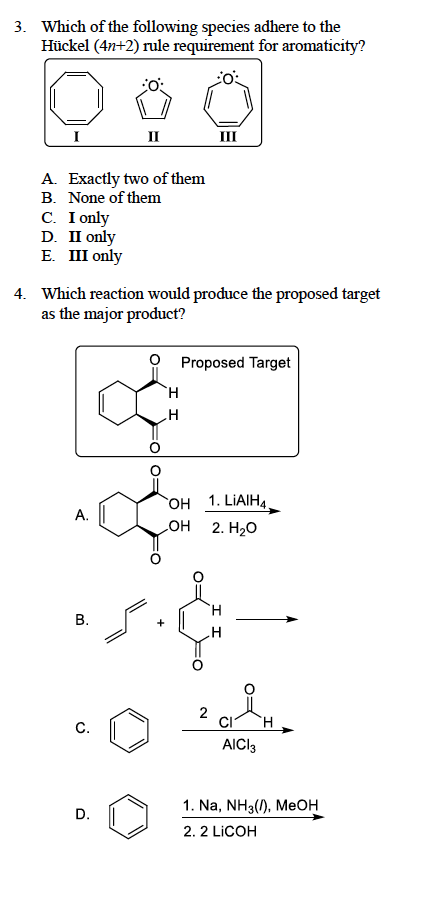


Solved 3 Which Of The Following Species Adhere To The Hu Chegg Com



Lecture 17 Chapter 15 Pdf Aromaticity Hckels 4n 2 Rule Only Applicable To Mono Cyclic Systems A Molecule Is Aromatic If 1 Every Atom In The Ring Has Course Hero



Slides Show
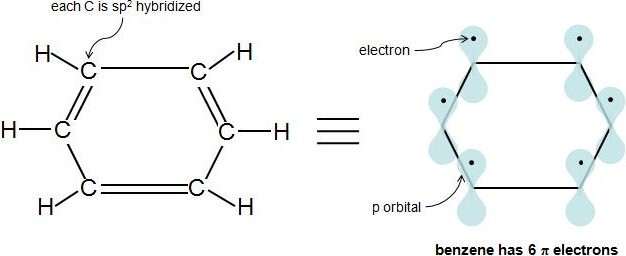.jpg?revision=1)


15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts



Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term



Aromaticity And Huckels Rule Powerpoint Slides
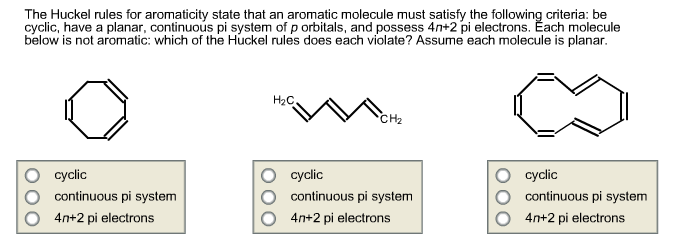


Solved The Huckel Rules For Aromaticity State That An Aro Chegg Com
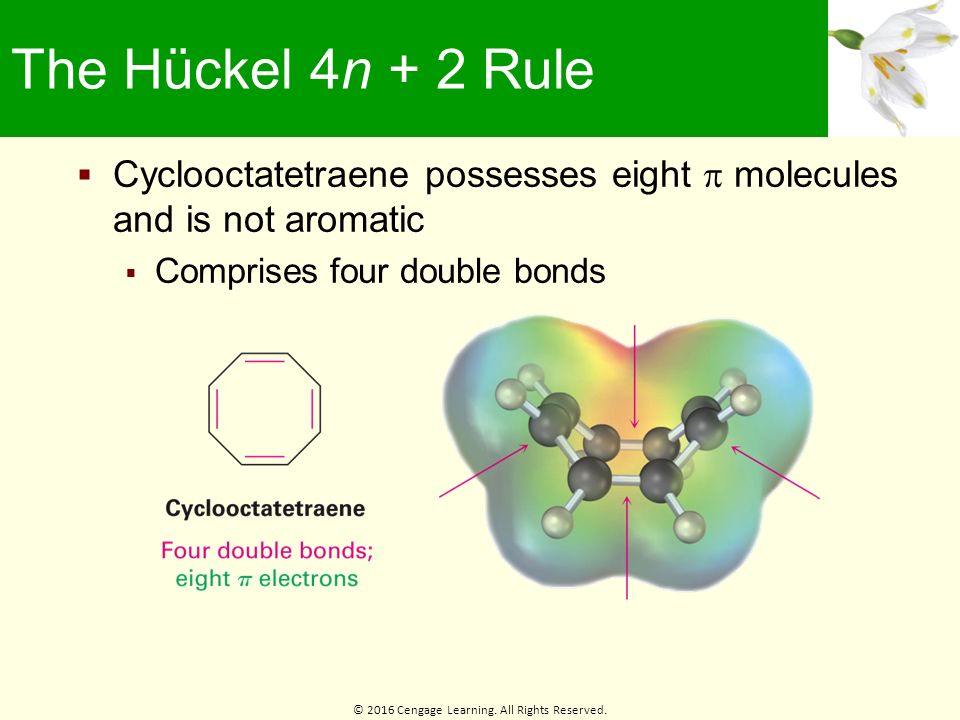


Chapter 15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Download


Sigmatropic Rearrangements Huckel Mobius Approach
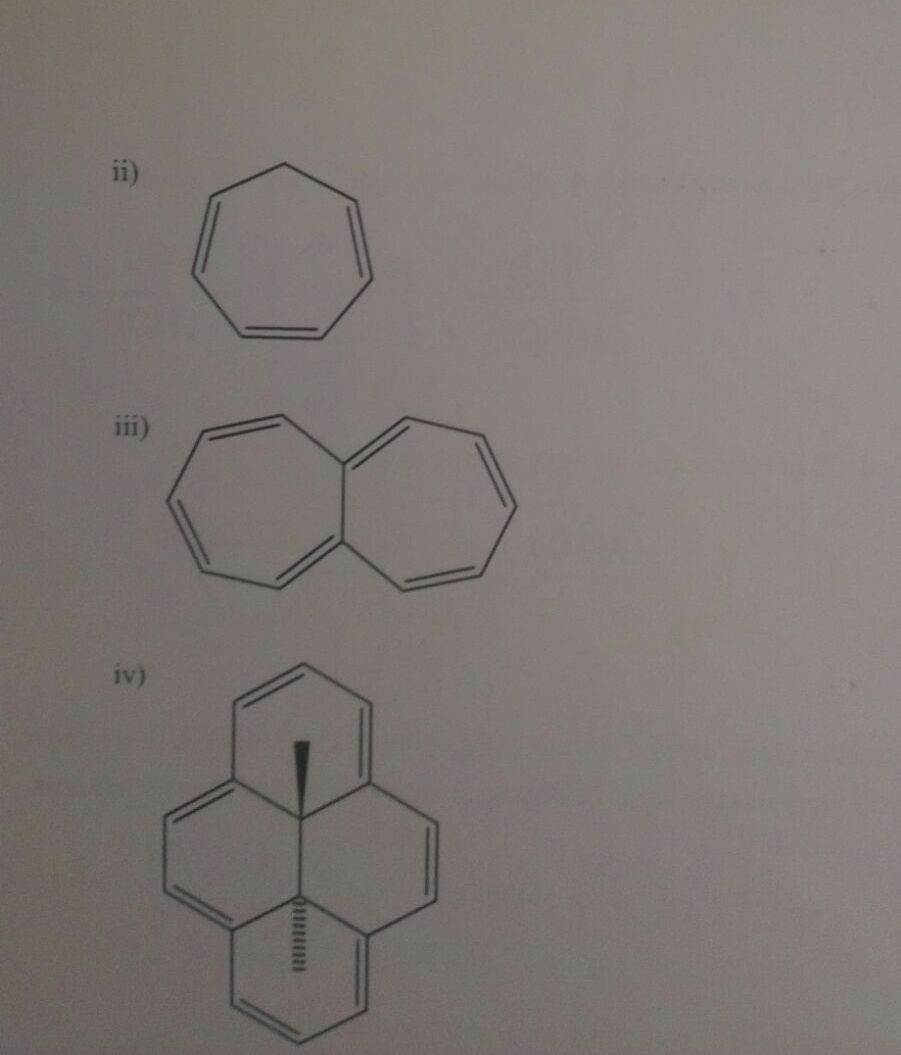


Solved Using The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Determine Whether Each Chegg Com


Antiaromaticity And Antiaromatic Compounds Master Organic Chemistry



15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts Aromaticity Covalent Bond


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
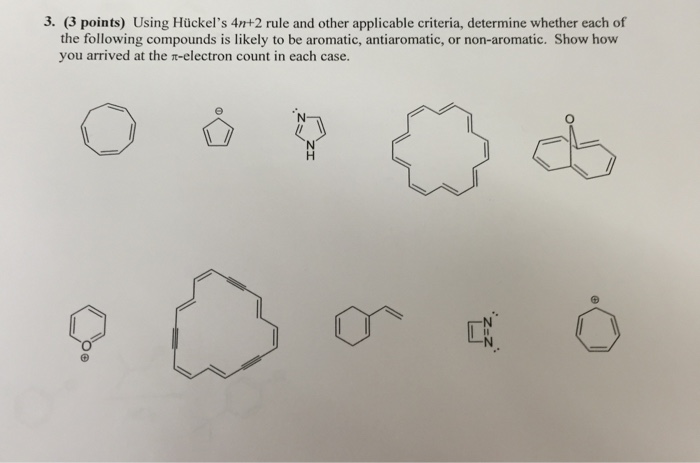


Solved Using Huckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cr Chegg Com
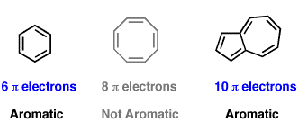


Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry



How Is Anthracene Aromatic Quora



Mobius Aromaticity Wikipedia
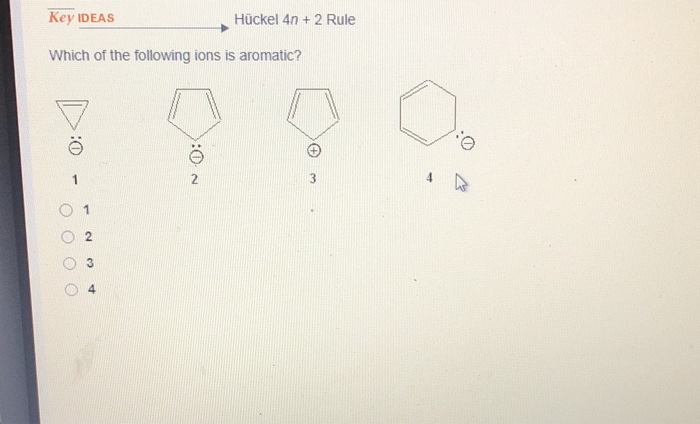


Solved Key Ideas Huckel 4n 2 Rule Which Of The Followin Chegg Com


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
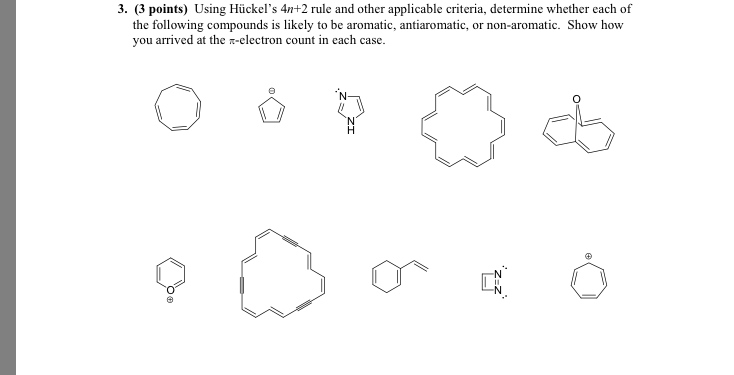


Solved Using Huckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cr Chegg Com



Aromatic Compounds Ppt Video Online Download
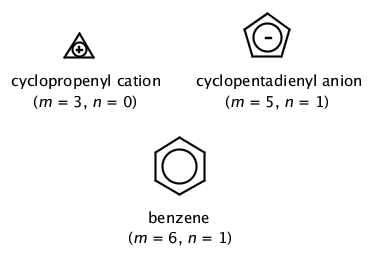


Iupac Huckel 4 Em N Em 2 Rule H



Huckel S Rule Explanation Of Huckel S 4n 2 Rule To Estimate Aromaticity



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps



Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
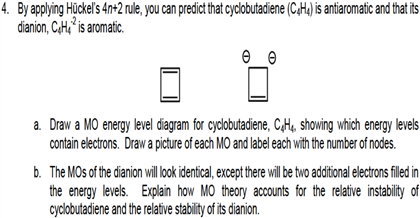


By Applying Huckel S 4n 2 Rule You Can Predict Th Chegg Com
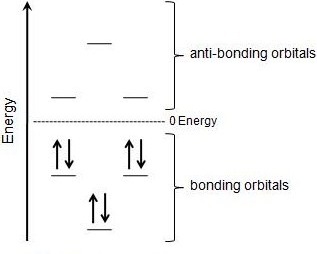.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=317&height=254)


Huckel S Rule Chemistry Libretexts


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term



Indicate Whether Or Not Each Of The Following Structures Is Considered To Be Aromatic Homeworklib
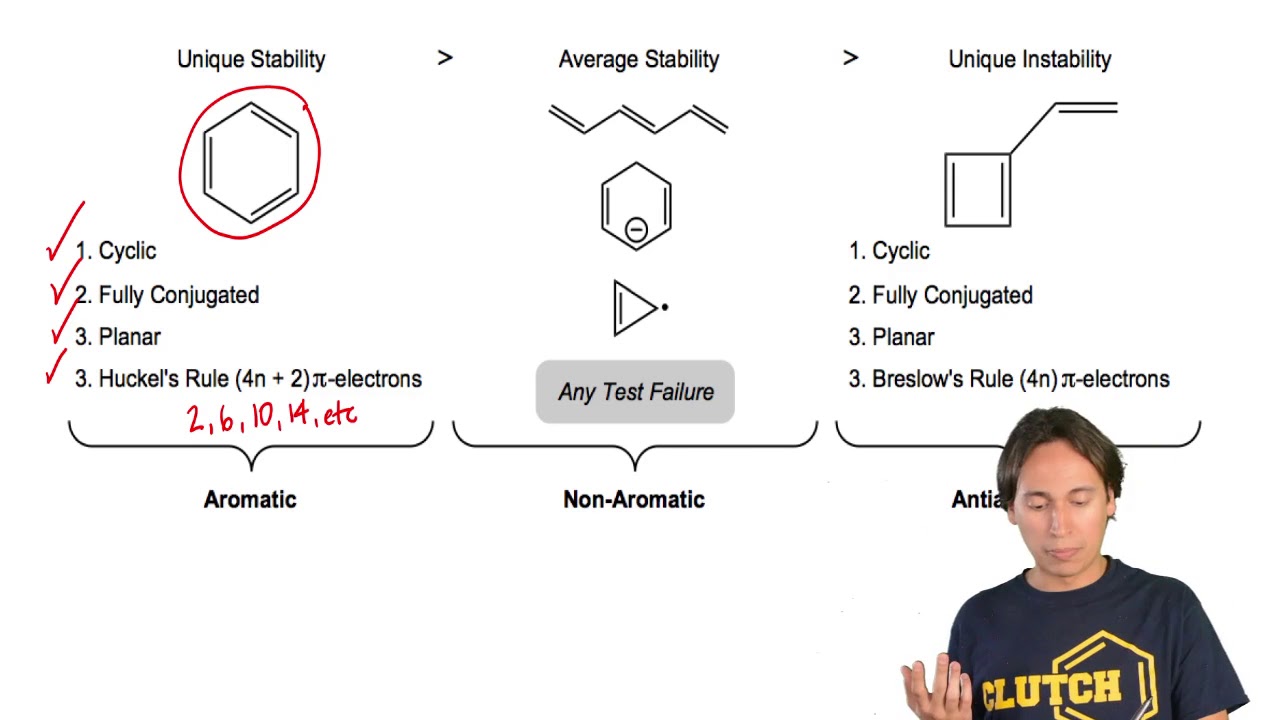


Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep



Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule 4n 2 Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule Aromaticity Youtube
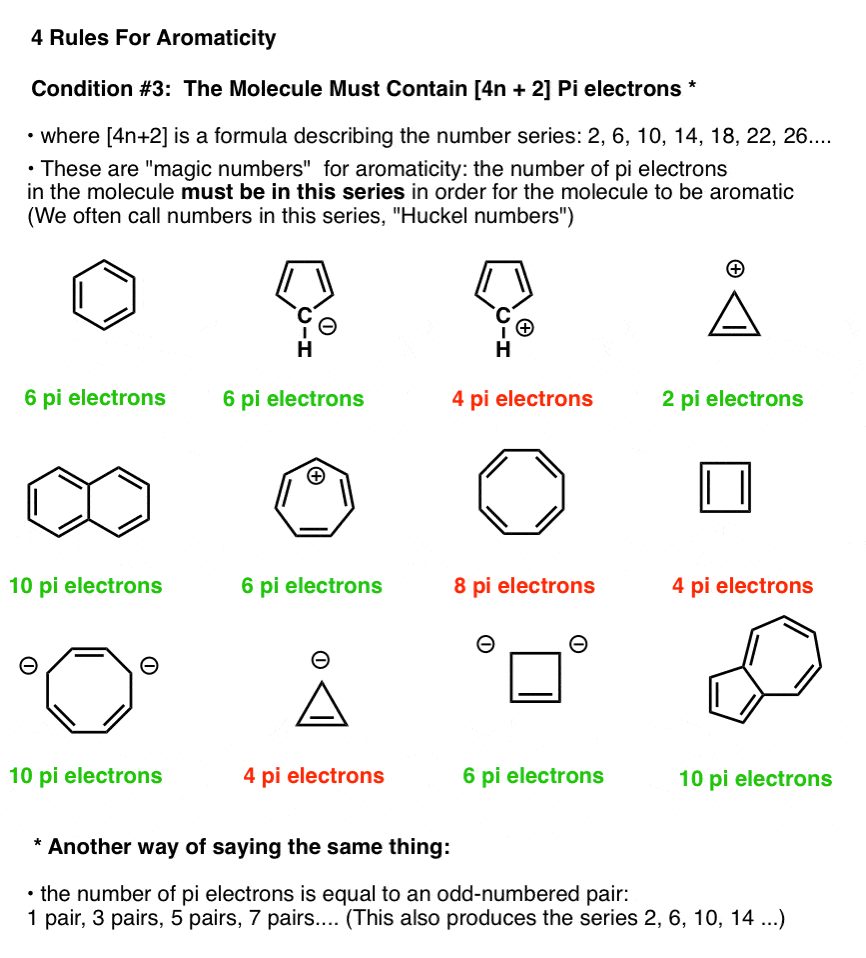


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
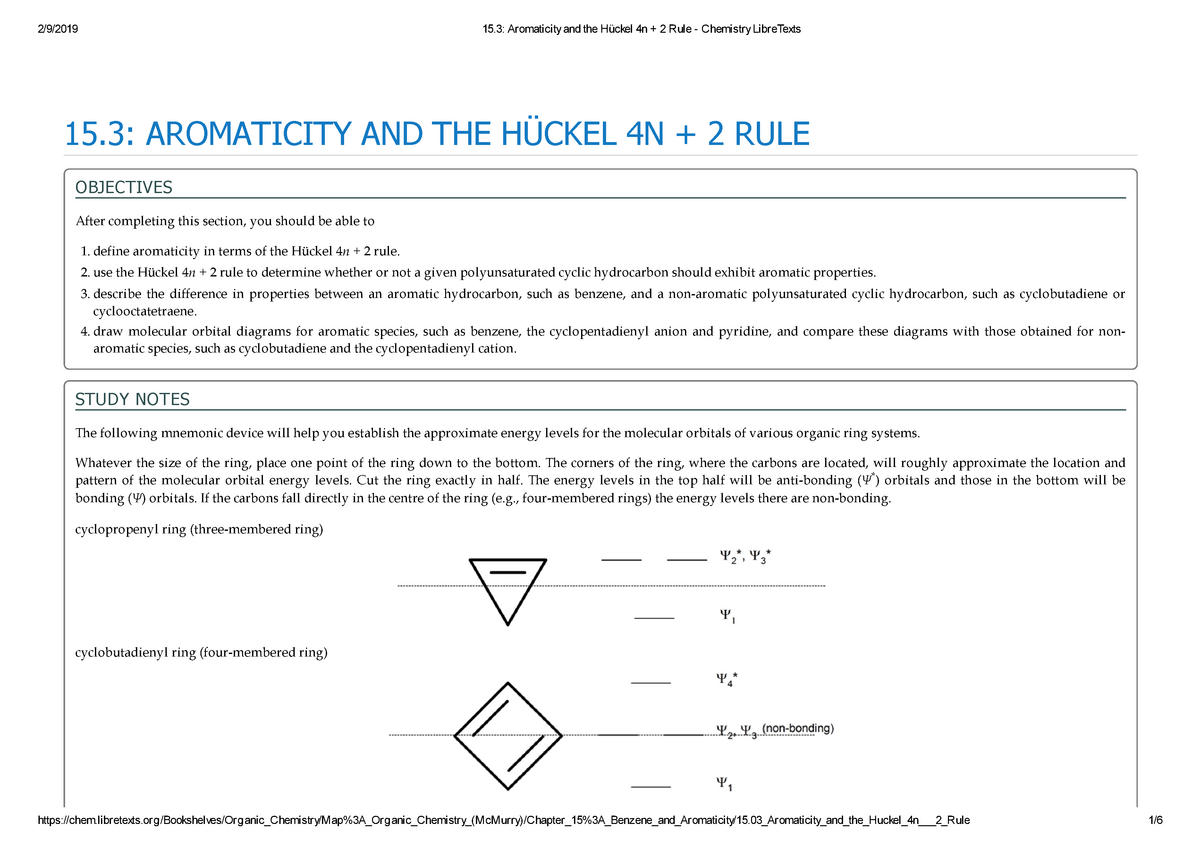


15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libre Texts 15 Aromaticity And The Ckel 4n Rule Objectives After Completing This Section You Should Be Studocu
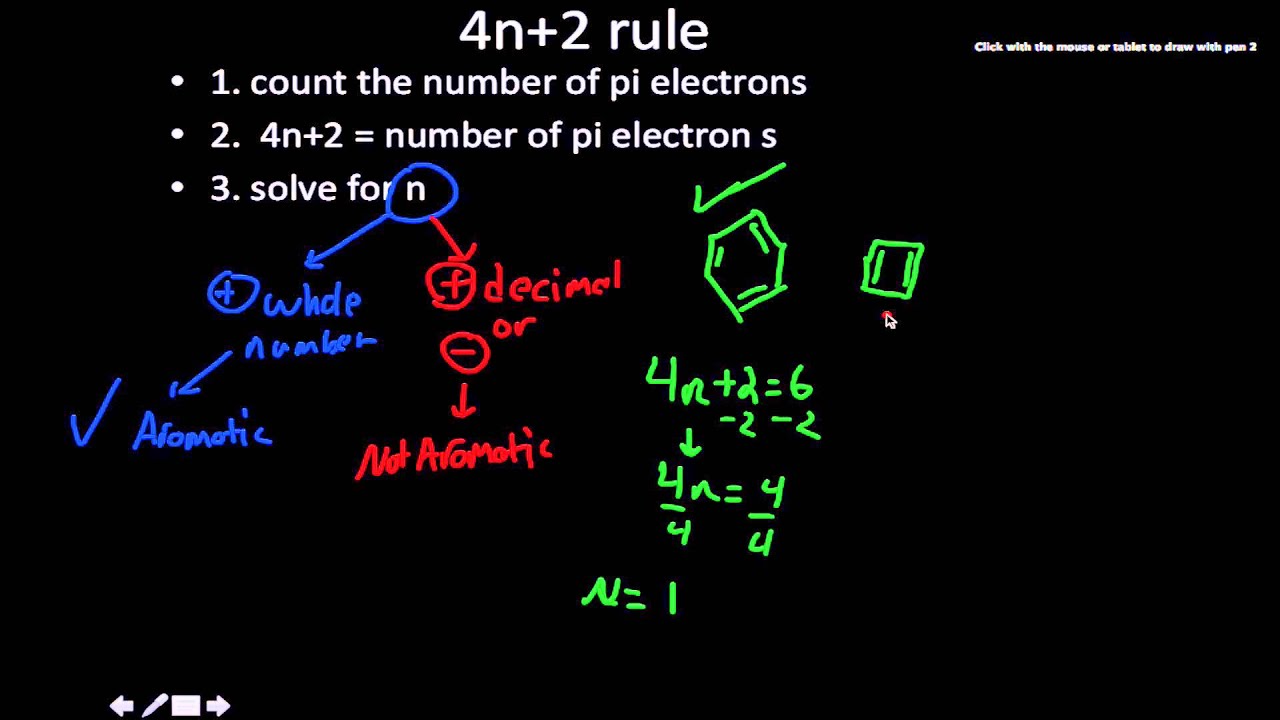


4n 2 Rule Youtube



Huckel Rule Or 4n 2 Rule For Aromaticity Examples And Exceptions Youtube
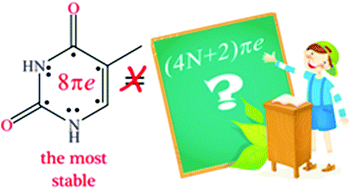


Tautomerisation Of Thymine Acts Against The Huckel 4n 2 Rule The Effect Of Metal Ions And H Bond Complexations On The Electronic Structure Of Thymine Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing


Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help
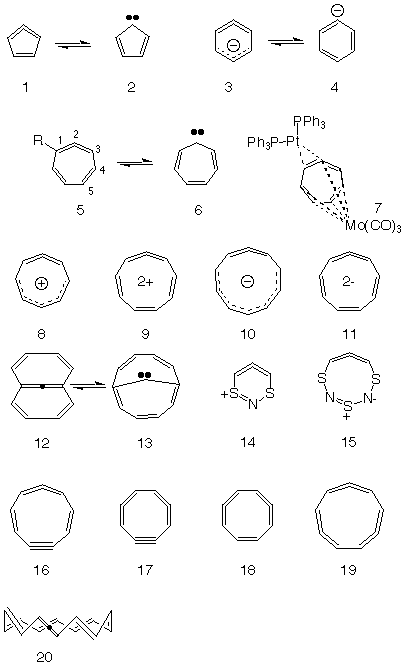


Mobius Aromatics Arising From A C C C Ring Component



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿